what are the various types of electric motors, including but not limited to dc motors?
Electrical motors tin exist found in many different applications, from common household items to diverse types of transportation and fifty-fifty advanced aerospace applications. Here, nosotros share a guide to provide you lot with a meliorate understanding of the options bachelor.
Electric Motors vs. Generators
Both electric motors and generators are electromagnetic devices with an armature winding or rotor, which rotates inside a field winding or stator; however, they have opposite functions. Generators convert mechanical free energy into electrical energy while motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
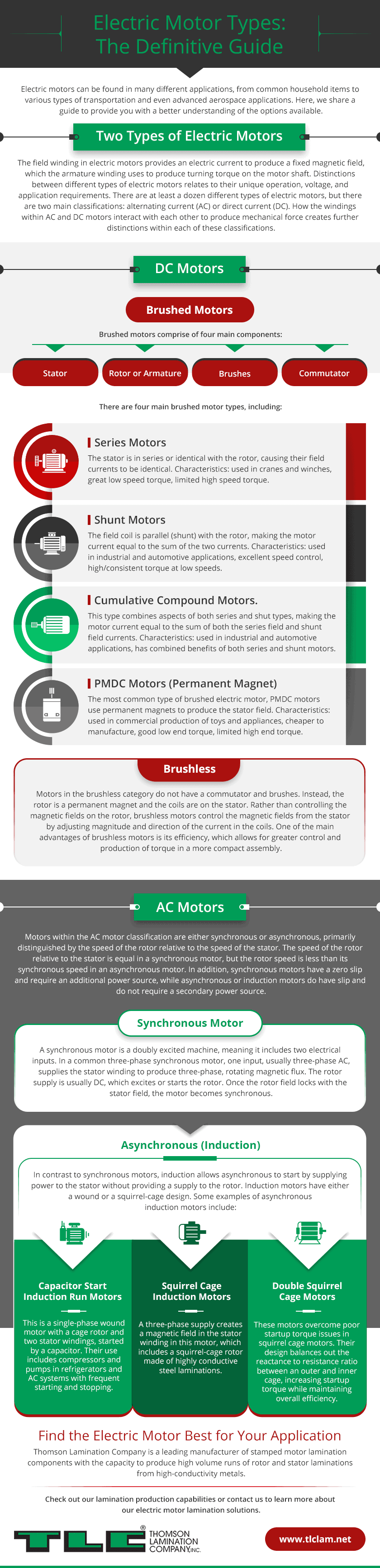
Two Types of Electric Motors
The field winding in electric motors provides an electrical current to produce a fixed magnetic field, which the armature winding uses to produce turning torque on the motor shaft. Distinctions between different types of electric motors relates to their unique operation, voltage, and application requirements. There are at least a dozen different types of electrical motors, but at that place are 2 primary classifications: alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). How the windings within Air-conditioning and DC motors interact with each other to produce mechanical force creates further distinctions inside each of these classifications.
DC Motors
Brushed Motors
Brushed motors comprise of iv master components:
- Stator
- Rotor or Armature
- Brushes
- Commutator
There are 4 main brushed motor types, including:
- Series Motors. The stator is in series or identical with the rotor, causing their field currents to be identical. Characteristics: used in cranes and winches, great low speed torque, express high speed torque.
- Shunt Motors. The field coil is parallel (shunt) with the rotor, making the motor current equal to the sum of the two currents. Characteristics: used in industrial and automotive applications, excellent speed control, high/consequent torque at depression speeds.
- Cumulative Compound Motors. This type combines aspects of both serial and shut types, making the motor current equal to the sum of both the series field and shunt field currents. Characteristics: used in industrial and automotive applications, has combined benefits of both serial and shunt motors.
- PMDC Motors (Permanent Magnet). The most common type of brushed electric motor, PMDC motors utilize permanent magnets to produce the stator field. Characteristics: used in commercial production of toys and appliances, cheaper to manufacture, expert low end torque, limited high finish torque.
Brushless
Motors in the brushless category practice not have a commutator and brushes. Instead, the rotor is a permanent magnet and the coils are on the stator. Rather than controlling the magnetic fields on the rotor, brushless motors control the magnetic fields from the stator by adjusting magnitude and direction of the current in the coils. One of the main advantages of brushless motors is its efficiency, which allows for greater command and production of torque in a more than compact assembly.
AC Motors
Motors within the AC motor classification are either synchronous or asynchronous, primarily distinguished by the speed of the rotor relative to the speed of the stator. The speed of the rotor relative to the stator is equal in a synchronous motor, but the rotor speed is less than its synchronous speed in an asynchronous motor. In addition, synchronous motors have a nada sideslip and require an boosted power source, while asynchronous or consecration motors do have slip and do not crave a secondary ability source.
Synchronous Motor
A synchronous motor is a doubly excited machine, meaning it includes two electrical inputs. In a common three-phase synchronous motor, i input, usually three-phase Air-conditioning, supplies the stator winding to produce three-phase, rotating magnetic flux. The rotor supply is unremarkably DC, which excites or starts the rotor. Once the rotor field locks with the stator field, the motor becomes synchronous.
Asynchronous (Induction)
In contrast to synchronous motors, induction allows asynchronous to start past supplying power to the stator without providing a supply to the rotor. Induction motors take either a wound or a squirrel-muzzle design. Some examples of asynchronous induction motors include:
- Capacitor Start Induction Run Motors. This is a unmarried-phase wound motor with a cage rotor and two stator windings, started by a capacitor. Their use includes compressors and pumps in refrigerators and AC systems with frequent starting and stopping.
- Squirrel Cage Consecration Motors. A three-phase supply creates a magnetic field in the stator winding in this motor, which includes a squirrel-cage rotor made of highly conductive steel laminations. They are depression cost, low maintenance, and loftier efficiency motors used in centrifugal pumps, industrial drives, big blowers and fans, machine tools, lathes, and other turning equipment.
- Double Squirrel Muzzle Motors. These motors overcome poor startup torque issues in squirrel muzzle motors. Their design balances out the reactance to resistance ratio between an outer and inner cage, increasing startup torque while maintaining overall efficiency.
Click to expand
Electrical Motor Identification
Selecting the motor best suited to a specific application depends upon meeting the needs of four characteristics:
- Horsepower and Speed
- Motor Frame
- Voltage Requirements
- Enclosures and Mounting Positions
A metallic nameplate fastened to the motor contains disquisitional data related to these characteristics with the exception of enclosure information.
Electric Motor Horsepower & Speed Rating
Both the horsepower rating and rotational speed rating (RPM) should friction match the load requirements for the installed awarding. Motors come up in different horsepower categories, including: fractional motors (one/20th HP to 1 HP), integral horsepower motors (ane HP to 400 HP), and large motors (100 HP to 50,000 HP). RPM ratings include 3600 RPM (2 pole), 1800 RPM (4 pole), and 1200 RPM (6 pole).
Electric Motor Frame
Motor frame size does not indicate its performance values, specially its horsepower rating. National Electrical Manufacturers Clan (NEMA) designed frame numbers to correspond to mounting sizes with their digits relating to their "D" dimension or the distance from center of shaft to center lesser of mount. In general, two-digit labels are for fractional motors, but larger horsepower motors can be congenital in them.
Voltage Requirements
Voltage, frequency, and stage are all a part of voltage requirements. In most N American and European cases, iii-phase motors include dual voltage displays like 230/460. The standard operating frequency for nigh electrical motors is threescore Hz, though fifty Hz motors are mutual in Europe. This variation in hertz indicates that the motor will operate at 5/half dozen of its normal RPM speed. Phase is the last scrap of information included with a motor's voltage requirements, indicating the type of supply required, such as three-stage, unmarried-phase and DC.
Enclosures and Mounting Positions
Enclosure data depends on the motor'southward installation surroundings. There are two main categories of enclosures—open motors and enclosed motors.
Open Motors
Applications for open motors include indoor locations that are relatively clean and dry, which is important since open motor enclosures permit air circulation through the windings.
Enclosed Motors
These types do not permit free air exchange betwixt the outside and interior of the motor. Variations in enclosure air-tightness and cooling features farther distinguish enclosed motor types, including:
- Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled (TEFC)
- Totally Enclosed Non-Ventilated (TENV)
- Totally Enclosed Air Over (TEAO)
- Totally Enclosed Wash Down (TEWD)
- Explosion-Proof Enclosures (EXPL)
- Hazardous Location (HAZ)
Find the Electric Motor Best for Your Awarding
Thomson Lamination Company is a leading manufacturer of stamped motor lamination components with the capacity to produce high volume runs of rotor and stator laminations from loftier-conductivity metals.
Check out our lamination production capabilities or contact united states of america to learn more about our electrical motor lamination solutions.
Source: https://www.tlclam.net/blog/electric-motor-types/
0 Response to "what are the various types of electric motors, including but not limited to dc motors?"
Postar um comentário